Hearing Test Galway
What to expect during your hearing test?
The hearing tests I perform in my Galway based practice are painless and non-invasive and are designed to measure your ability to hear different sounds, pitches, and frequencies.
Firstly I focus on your medical case history by asking questions about your general health including hearing health and how you feel you are hearing.
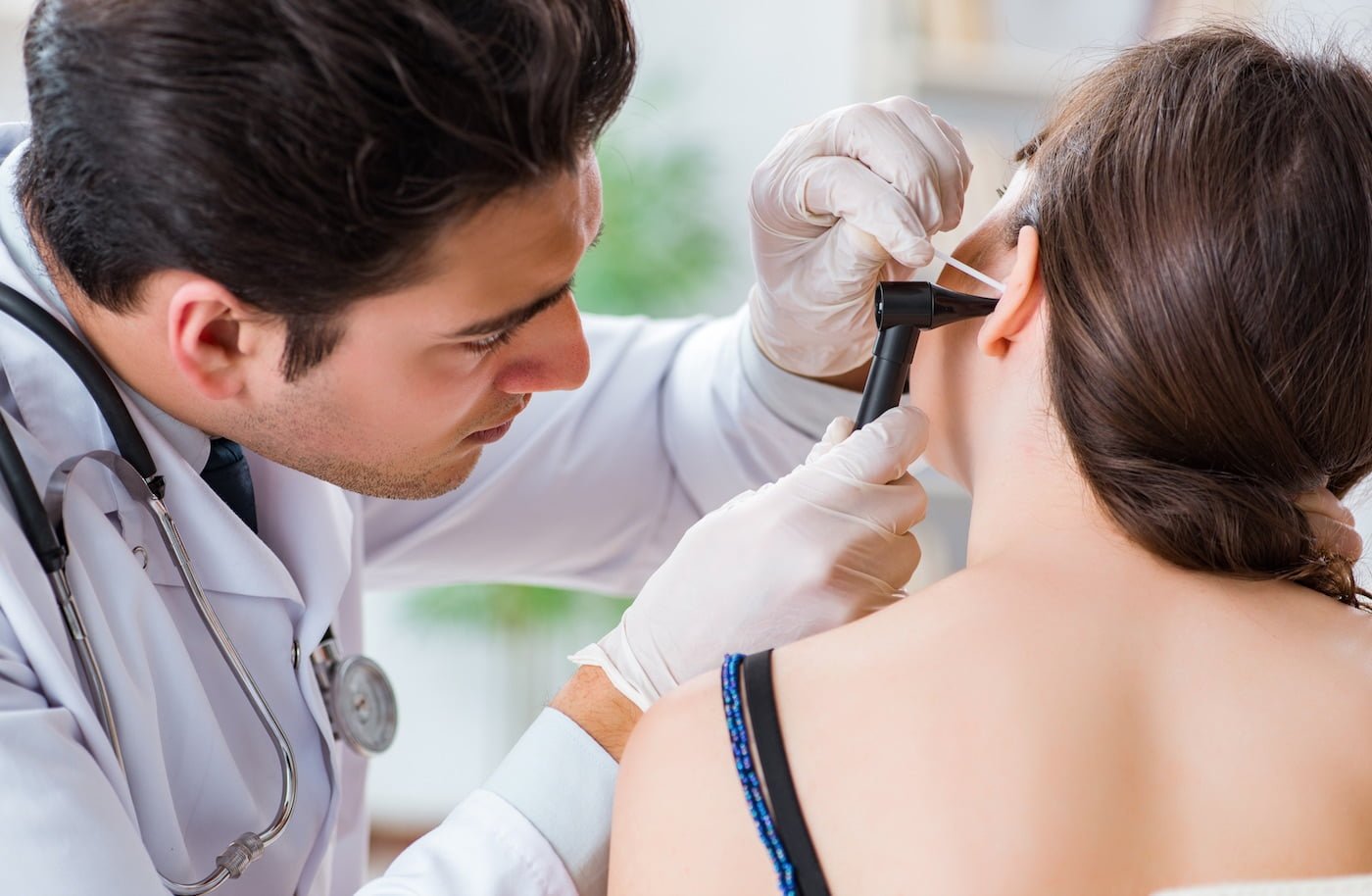
I then examine your ear canal and use an otoscopic camera to display a clear photograph of your ear drum before I do the audiometric assessment.
I discuss, with you, your everyday listening environments to ascertain where and why you are having difficulty hearing. I will then continue onto the audiometric test by presenting to you, through a set of headphones, a range of calibrated sounds.
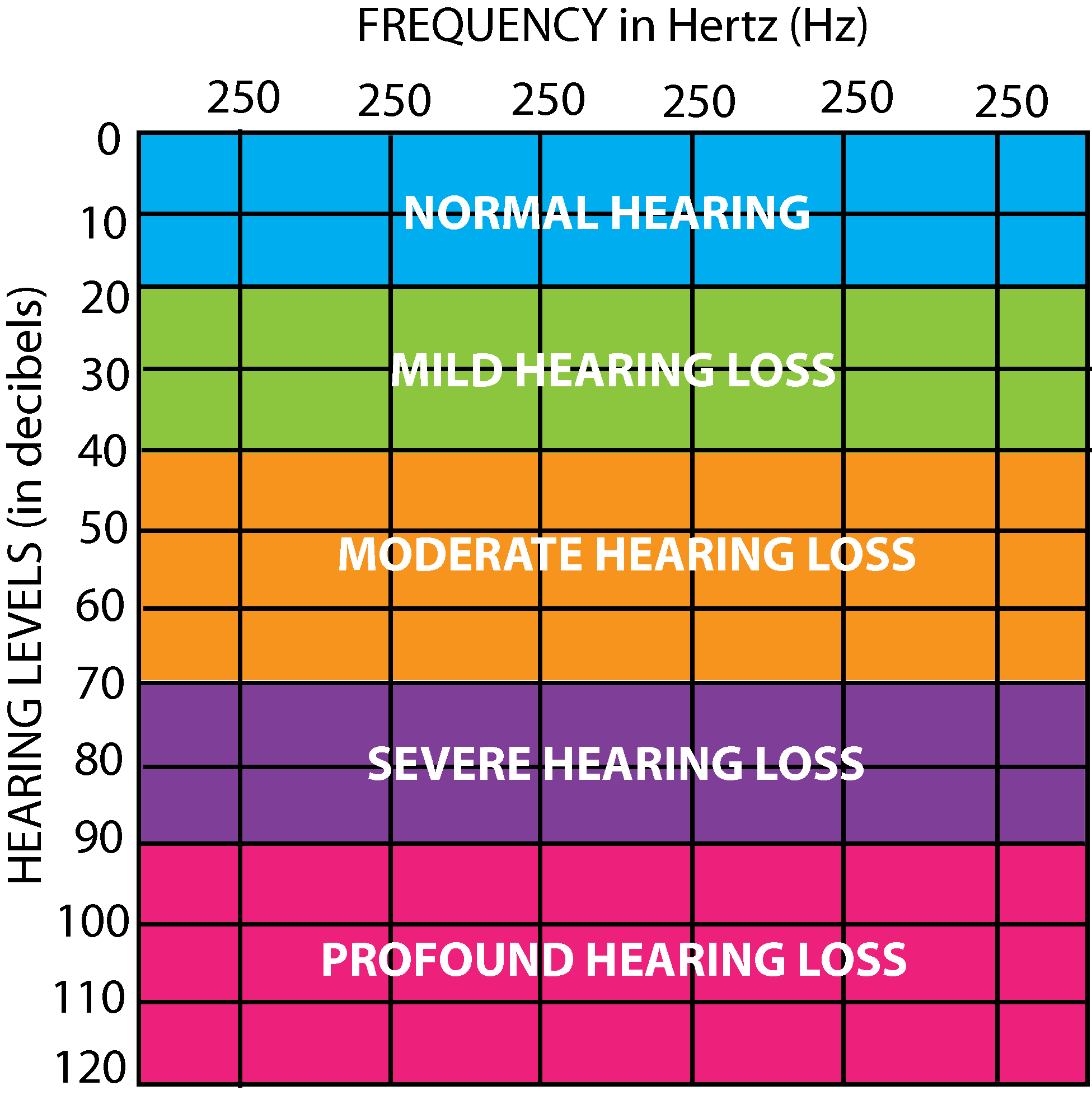
The audiometer produces sounds and tones of various levels and frequencies, which are transmitted to each individual ear. I will chart the loudness on the audiogram which is a graphical representation of how well your ear responds to different levels of frequencies. You will be asked to raise your hand or press a button whenever you hear sound being sent to your ears. I will record all the information received and analyse it. The extent of your hearing loss is based on the frequencies you could and could not hear.
The Audiometry Test
The audiometry test measures the softest, or least audible, sound that a person can hear. The loudness of sound is measured in decibels (dB). A whisper is about 20 dB, loud music ranges 80-120 dB, and a jet engine is about 180 dB. The tone of sound is measured in frequencies (Hz). Low bass tones range 50-60 Hz, high-pitched tones range 10,000 Hz or higher. Normal hearing range is 250- 8,000 Hz at 25 dB or lower.
The Tympanometry Test
A tympanometry test detects pressure in the Middle ear and diagnoses problems such as fluid/wax build up, perforated eardrum, ossicle bone damage, or Acoustic Neuroma tumours in the middle ear. Acoustic reflex testing evaluates the cranial nerves and brainstem. To perform a Tympanometry test, a device is placed into your ear.
This device changes the air pressure in your ear and makes the eardrum move back and forth. A calibrated machine records the results on a graph called a tympanogram. A speech test assesses a person’s ability to understand speech in background noise. If your speech discrimination is poor, speech may sound muffled and unclear. Word recognition scores can be helpful in predicting the usefulness of a hearing aid. I will then give you a comprehensive summary of the audiometric test results and if I confirm a hearing loss, I will advise the best technology to suit your hearing needs.
There is never an obligation to purchase. If you feel you would like to try hearing aids, I will programme a pair of demo digital hearing instruments to give you an understanding of how you could benefit from wearing them. I also recommend that you bring a trusted support person to the consultation. I often recommend a live demo wearing hearing aids in a local coffee shop. The benefit of hearing aids is best assessed with a trusted familiar voice.
